思考:
- 讲讲 RunLoop,项目中有用到吗?
- RunLoop 内部实现逻辑?
- RunLoop 和线程的关系?
- timer 与 RunLoop 的关系?
- 程序中添加每3秒响应一次的 NSTimer,当拖动 tableview 时 timer 可能无法响应要怎么解决?
- RunLoop 是怎么响应用户操作的, 具体流程是什么样的?
- 说说 RunLoop 的几种状态
- RunLoop 的 mode 作用是什么?
什么是 RunLoop
顾名思义:运行循环,在程序运行过程中循环做一些事情。
应用范畴:
- 定时器(Timer)、PerformSelector
- GCD Async Main Queue
- 事件响应、手势识别、界面刷新
- 网络请求
- AutoreleasePool

如果没有 RunLoop
打印完“Hello, World!”后,执行完 return 方法会退出程序:
如果有了 RunLoop
程序并不会马上退出,而是保持运行状态。UIApplicationMain() 方法的内部创建了 RunLoop:
RunLoop 的基本作用
- 保持程序的持续运行
- 处理App中的各种事件(比如触摸事件、定时器事件等)
- 节省CPU资源,提高程序性能:该做事时做事,该休息时休息
……
RunLoop 的实现原理(伪代码)
|
|
RunLoop 对象
获取 RunLoop 对象
iOS 中有2套 API 来访问和使用 RunLoop:
- Foundation:NSRunLoop
- Core Foundation:CFRunLoopRef
Foundation
打印结果:
因为是在主线程打印的,所以 +currentRunLoop 和 +mainRunLoop 获取的都是主线程的 RunLoop。
Core Foundation
打印结果:
因为是在主线程打印的,所以 CFRunLoopGetCurrent() 和 CFRunLoopGetMain() 获取的都是主线程的 CFRunLoopRef。
从打印结果可以看出,上面种方式在获取主线程的 RunLoop 时获取到的 NSRunLoop 和 CFRunLoopRef 内存地址不一样。NSRunLoop 和 CFRunLoopRef 都代表着 RunLoop 对象,但是 NSRunLoop 是基于 CFRunLoopRef 的一层 OC 包装,真正的 RunLoop 是里面的 CFRunLoopRef(如:NSArray 是基于 CFArrayRef 的封装,NSString 是基于 CFStringRef 的封装)。
RunLoop 与线程
- 每条线程都有唯一的一个与之对应的 RunLoop 对象;
- RunLoop 保存在一个全局的 Dictionary 里,线程作为 key,RunLoop 作为 value;
- 线程刚创建时并没有 RunLoop 对象,RunLoop 会在第一次获取它时创建;
- RunLoop 会在线程结束时销毁;
- 主线程的 RunLoop 已经自动获取(创建),子线程默认没有开启 RunLoop;
CFRunLoopRef 是开源的,下载 CF-1153.18 。找到 CFRunLoop.c 文件里的 _CFRunLoopGet0() 方法:
从源码里可以看到线程和 RunLoop 之间是一一对应的,其关系是保存在一个全局的 Dictionary 里。_CFRunLoopGet0() 先调用 CFDictionaryGetValue() 方法,以线程 pthreadPointer(t) 为 key 在 __CFRunLoops 里查找 loop。如果 loop 不存在,再通过 __CFRunLoopCreate() 方法创建新的 newLoop,并以线程 pthreadPointer(t) 为 key,newLoop 为 value 保存到 __CFRunLoops 里。
RunLoop 相关的类
Core Foundation 中关于 RunLoop 的5个类:
- CFRunLoopRef
- CFRunLoopModeRef
- CFRunLoopSourceRef
- CFRunLoopTimerRef
- CFRunLoopObserverRef
查看 RunLoop 源码,找到 CF-1153.18 里的 RunLoop.c 文件:
CFRunLoopRef
CFRunLoopRef:RunLoop 类对象的结构体。
精简版
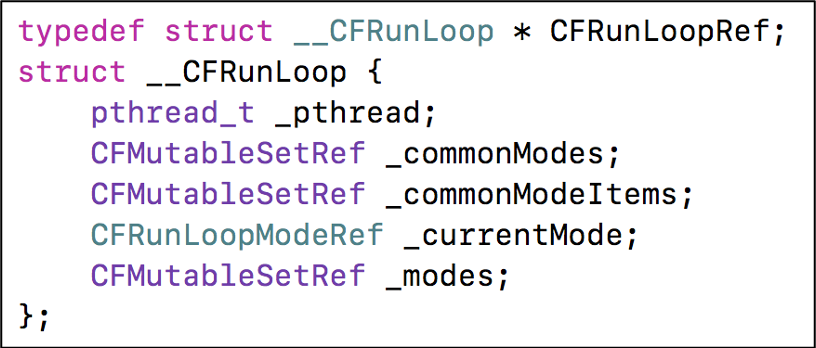
_pthread:__CFRunLoop 对应的线程。
_currentMode:当前的 CFRunLoopModeRef。
_modes:装着 CFRunLoopModeRef 的集合。
CFRunLoopModeRef 代表 RunLoop 的运行模式。RunLoop 启动时只能选择其中一个 Mode,作为 _currentMode。如果需要切换 Mode,只能退出当前 Loop,再重新选择一个 Mode 进入。
一个 RunLoop 包含若干个 Mode,每个 Mode 又包含若干个 Sources0/Sources1/Timer/Observer。不同组(不同mode)的 Sources0/Sources1/Timer/Observer 能分隔开来,互不影响。
👉 注意:如果 Mode 里没有任何 Sources0/Sources1/Timer/Observer,RunLoop 会立马退出。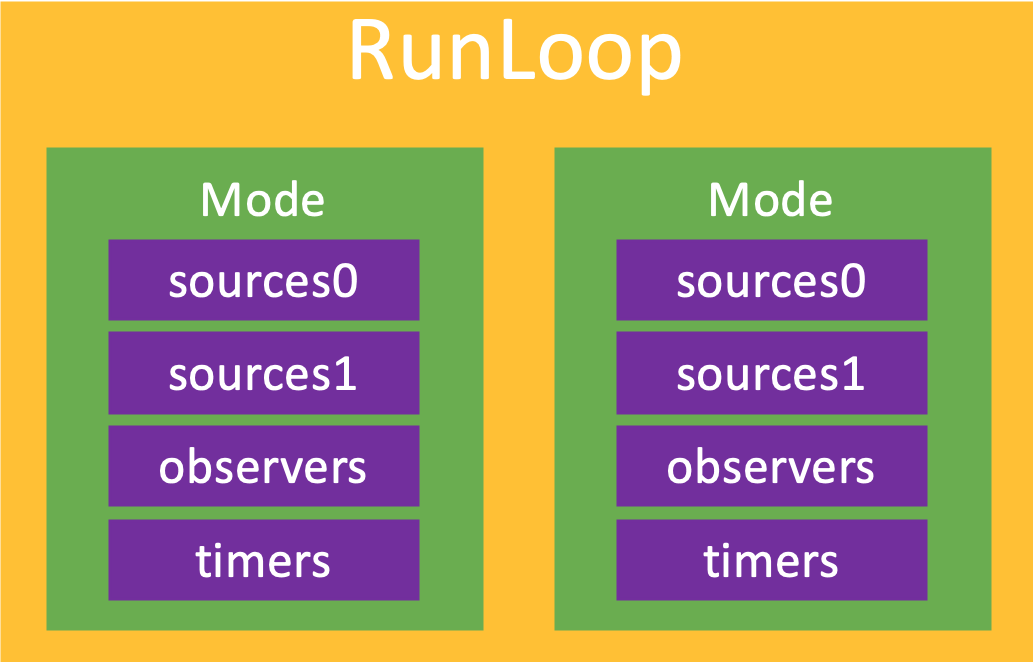
CFRunLoopModeRef
CFRunLoopModeRef:RunLoop 的运行模式。
精简版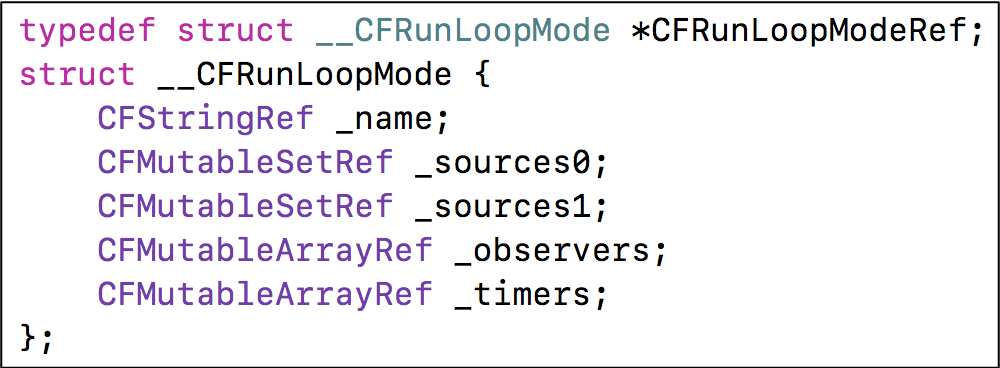
_sources0:装着 CFRunLoopSourceRef 的集合。
_sources1:装着 CFRunLoopSourceRef 的集合。
_observers:装着 CFRunLoopObserverRef 的集合。
_timers:装着 CFRunLoopTimerRef 的集合。
RunLoop 在选择了某一种模式作为当前模式后,就开始处理当前模式里的 Source0/Source1/Timer/Observer 事件了:
- Source0:触摸事件、
performSelector:onThread:方法 - Source1:基于 Port 的线程间通信、系统事件捕捉
- Timers:NSTimer、
performSelector:withObject:afterDelay:方法 - Observers:用于监听 RunLoop 的状态、UI 刷新(BeforeWaiting)、Autorelease pool(BeforeWaiting)
RunLoop 将 OC 代码转换成了 Sources0/Sources1/Timer/Observer,并且循环监测并执行它们。比如 UI 的刷新和Autorelease pool 的自动释放都是在进入休眠前完成的。
CFRunLoopSourceRef
|
|
触摸事件:
在断点处打印函数调用栈: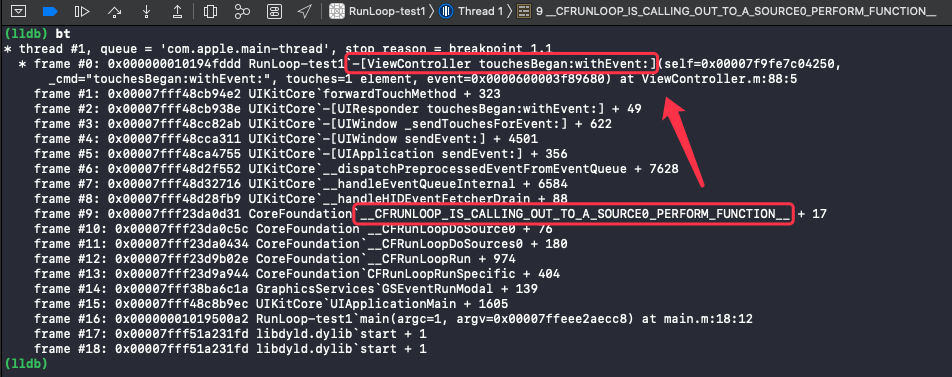
在打印出的函数调用栈里可以看到该事件是由 __CFRUNLOOP_IS_CALLING_OUT_TO_A_SOURCE0_PERFORM_FUNCTION__ 调用过来的。触摸事件先是由 Sources1 捕捉到后传递给 Sources0。
CFRunLoopObserverRef
实现:
__CFRunLoopObserver 的 _activities 是一个枚举,包含以下状态:
CFRunLoopObserverCreateWithHandler()
使用 CFRunLoopObserverCreateWithHandler() 方法监听 RunLoop:
点击事件唤醒 RunLoop
|
|
点击屏幕打印结果:
从打印结果可以看到,在处理点击事件前,RunLoop 先进入到了 kCFRunLoopBeforeSources 状态,表明即将处理 sources。
NSTimer 唤醒 RunLoop
|
|
点击屏幕打印结果:
从打印结果可以看到,RunLoop 在17秒处进入了 kCFRunLoopBeforeWaiting(休眠)状态,20秒处进入了 kCFRunLoopAfterWaiting(唤醒)状态,同时执行了代码块打印出了结果。
CFRunLoopObserverCreate()
使用 CFRunLoopObserverCreate() 方法监听 RunLoop:
常见的2种 Mode
kCFRunLoopDefaultMode(NSDefaultRunLoopMode):App 的默认 Mode,通常主线程是在这个 Mode 下运行。
UITrackingRunLoopMode:界面跟踪 Mode,用于 ScrollView 追踪触摸滑动,保证界面滑动时不受其他 Mode 影响。(只有主线程需要考虑这种 mode)
RunLoop 的模式切换:
添加监听后,在页面上添一个 UITextView。
开始滚动 UITextView 时的打印:
停止滚动 UITextView 时的打印:
从打印结果可以看到,操作 textView 时 RunLoop 进行了模式切换:
在开始滚动 textView 时,RunLoop 先退出了 kCFRunLoopDefaultMode 再进入了 UITrackingRunLoopMode。
在停止滚动 textView 时,RunLoop 先退出了 UITrackingRunLoopMode 再进入 kCFRunLoopDefaultMode。
RunLoop 源码分析
RunLoop 执行流程图: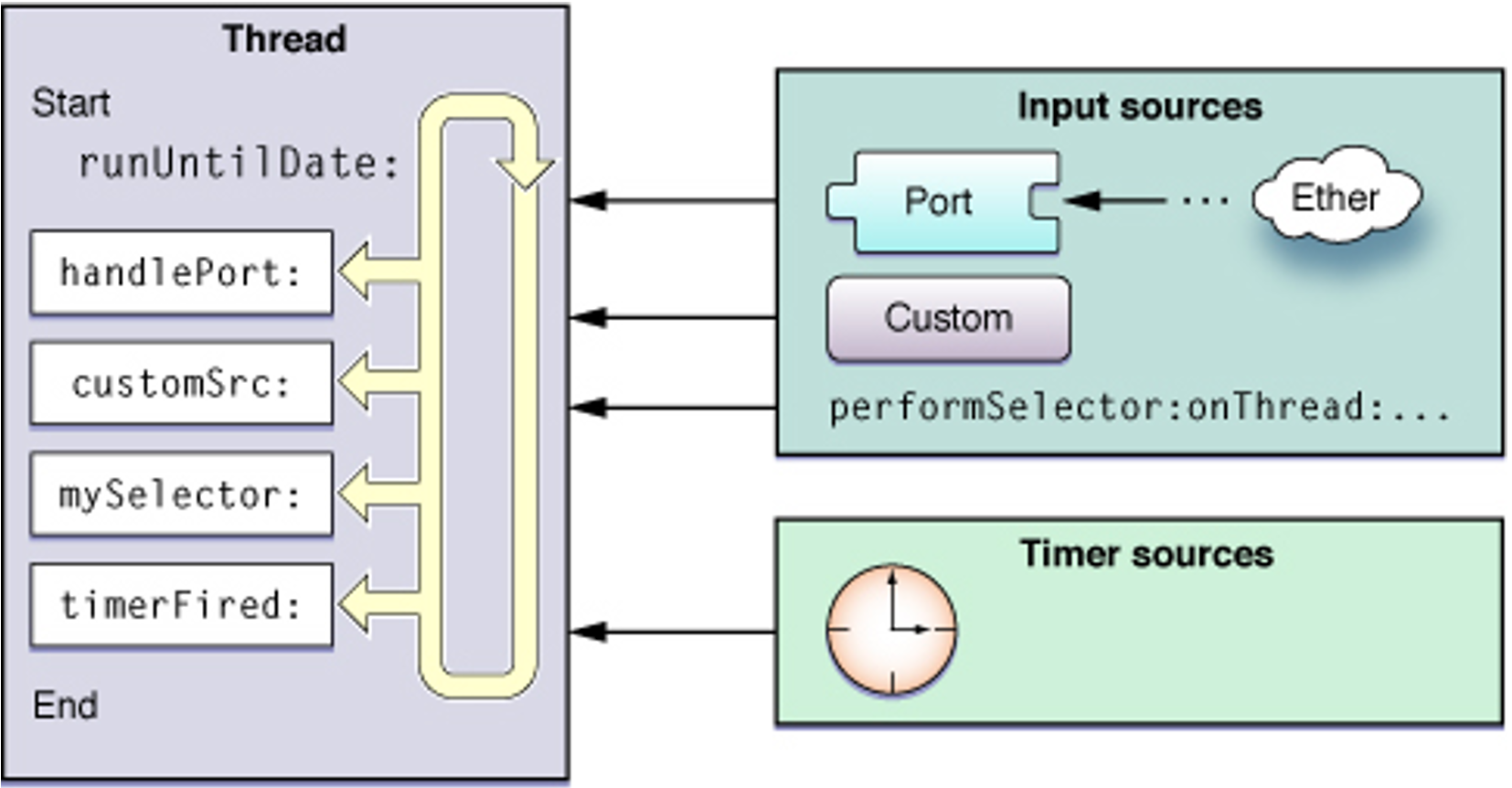
RunLoop 的实现原理
找到 RunLoop 的入口:
断点处查看函数调用栈: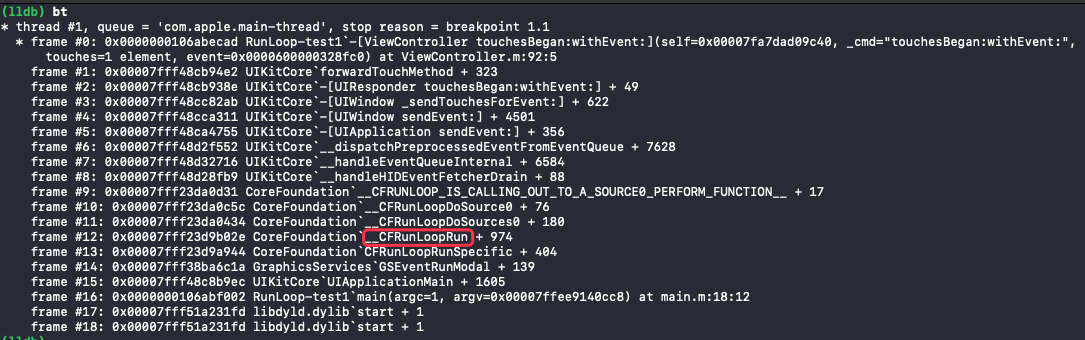
从图中可以看到,RunLoop 先通过 CFRunLoopRunSpecific() 方法调用了 __CFRunLoopRun() 方法,__CFRunLoopRun 方法调用了 __CFRunLoopDoSources0() 方法,所以 CFRunLoopRunSpecific 就是 RunLoop 的入口。
CFRunLoopRunSpecific
实现:
简化后:
CFRunLoopRunSpecific() 方法内部调用了 __CFRunLoopRun() 方法来实现 RunLoop 的具体处理逻辑。
__CFRunLoopRun
在 CF-1153.18 找到 RunLoop.c 文件,再找到 __CFRunLoopRun() 方法。简化后:
可以看到 RunLoop 主要做了以下6件事(有序):
__CFRunLoopDoObservers()通知 observers__CFRunLoopDoBlocks()处理 blocks__CFRunLoopDoSources0()处理 sources0__CFRunLoopDoTimers()处理 timers__CFRUNLOOP_IS_SERVICING_THE_MAIN_DISPATCH_QUEUE__()处理 GCD__CFRunLoopDoSource1()处理 sources1
除了处理 GCD 的方法外,其它的5个方法,在调用到 Foundation 框架的函数前,还会调用一个 Core Foundation 框架的函数:
__CFRunLoopDoObservers()
|
|
函数调用栈: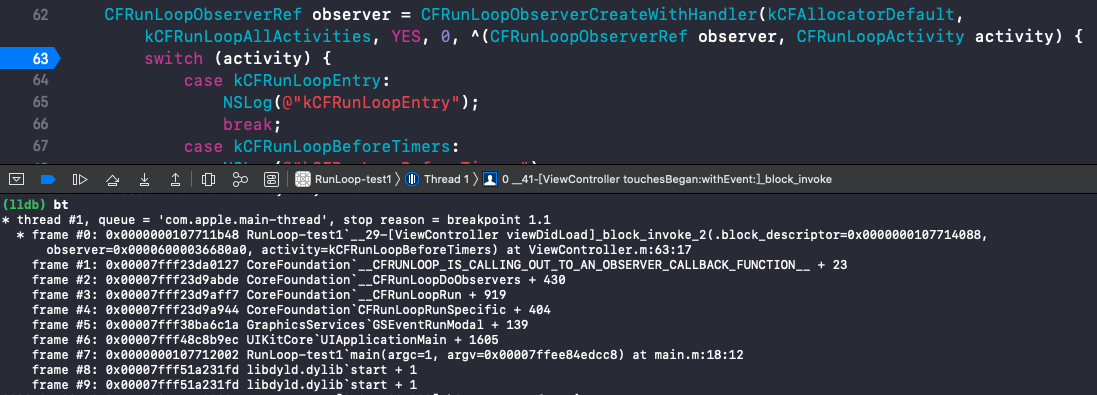
__CFRunLoopDoBlocks()
内部调用的是 __CFRUNLOOP_IS_CALLING_OUT_TO_A_BLOCK__() 方法:
函数调用栈: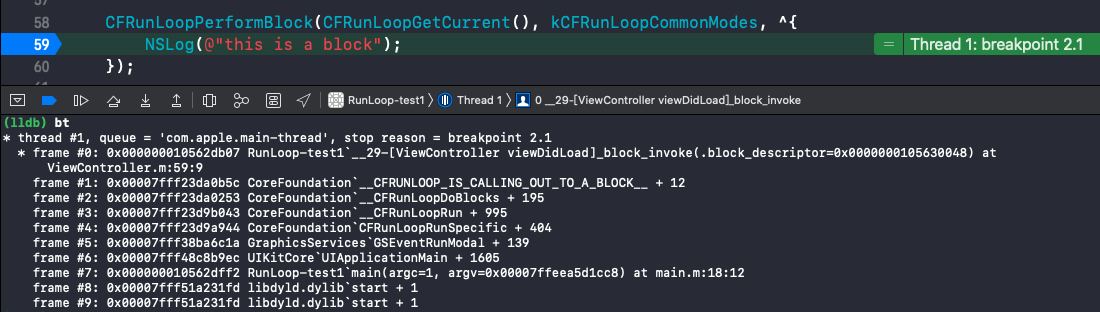
__CFRunLoopDoSources0()
内部调用的是 __CFRUNLOOP_IS_CALLING_OUT_TO_A_SOURCE0_PERFORM_FUNCTION__() 方法:
函数调用栈: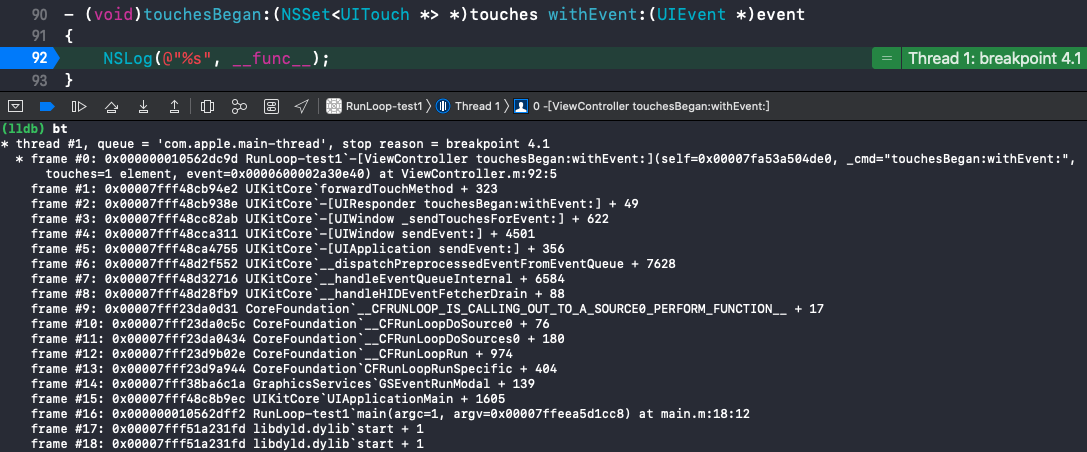
__CFRunLoopDoTimers()
内部调用的是 __CFRUNLOOP_IS_CALLING_OUT_TO_A_TIMER_CALLBACK_FUNCTION__() 方法:
函数调用栈: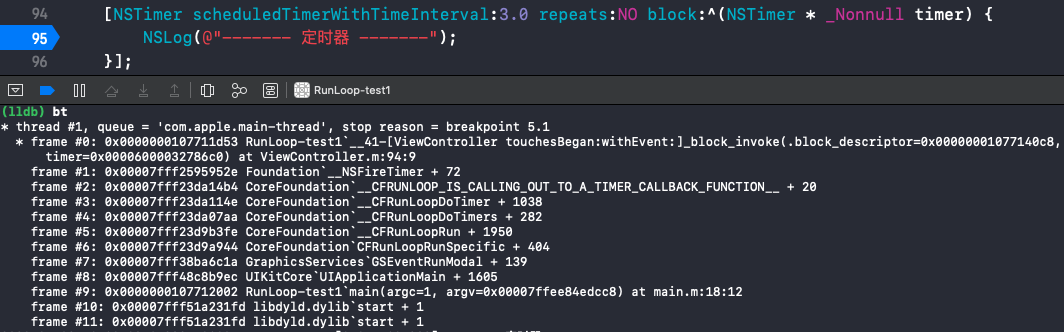
__CFRunLoopDoSource1()
内部调用的是 __CFRUNLOOP_IS_CALLING_OUT_TO_A_SOURCE1_PERFORM_FUNCTION__() 方法:
__CFRUNLOOP_IS_SERVICING_THE_MAIN_DISPATCH_QUEUE__
|
|
GCD 和 RunLoop 是相对独立的,只在一种情况下会调用到 RunLoop 的 __CFRUNLOOP_IS_SERVICING_THE_MAIN_DISPATCH_QUEUE__() 方法: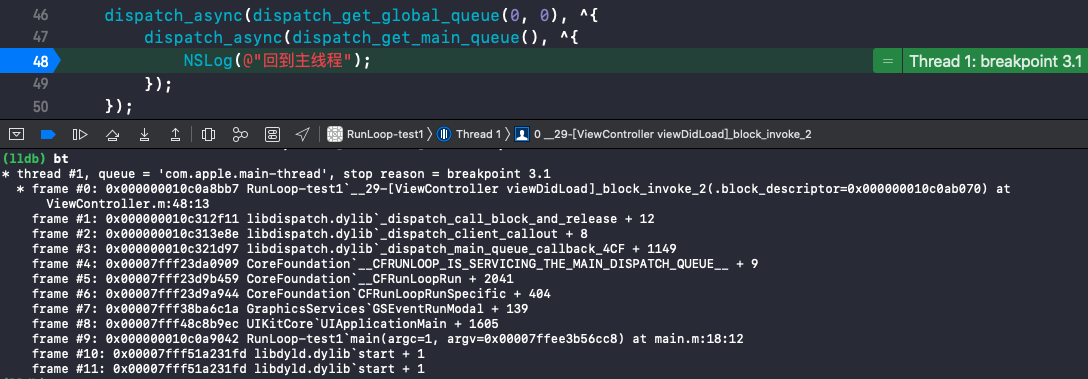
文字版流程图
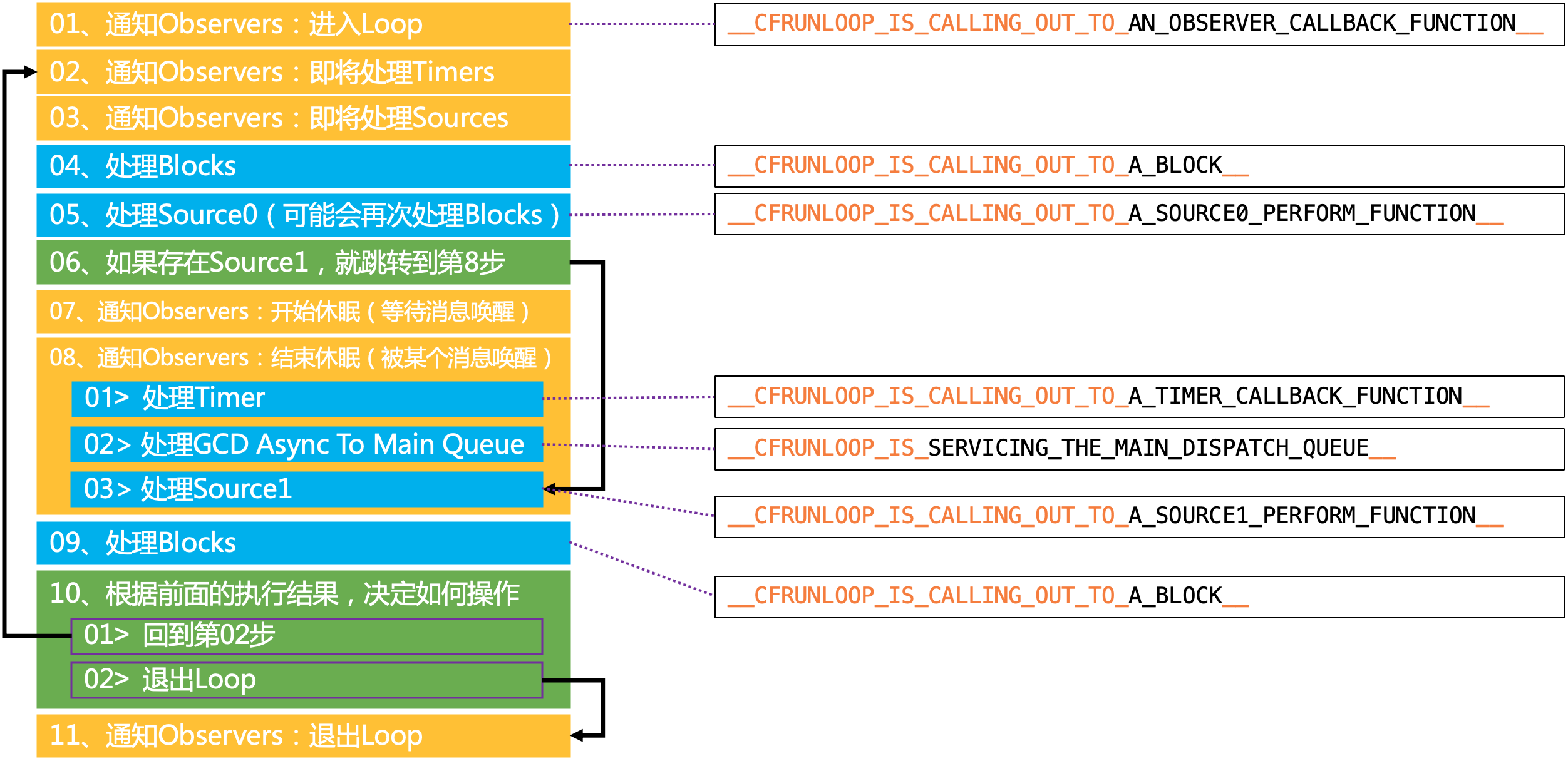
图中的 block 是通过 CFRunLoopPerformBlock() 添加的任务。
RunLoop 休眠的实现原理
|
|
在 __CFRunLoopRun() 方法中调用了 __CFRunLoopServiceMachPort() 方法,__CFRunLoopServiceMachPort() 方法内部又调用了 mach_msg() 方法,使得 RunLoop 进入休眠状态。此时当前线程不再执行,while 循环会停止在 __CFRunLoopServiceMachPort() 方法这里,同时 RunLoop 会释放在 CPU 占用的资源,不再执行任何代码,直到有消息唤醒时才会继续执行当前线程(while 循环,以及 while 循环下面省略掉的代码),充分做到了节省资源。RunLoop 就是这样一个函数,其内部是一个 do-while 循环。当你调用 CFRunLoopRun() 时,线程就会一直停留在这个循环里;直到超时或被手动停止,该函数才会返回。
mach_msg() 方法会调用到内核层级的 API,该 API 对应的函数主要功能是等待消息,实现逻辑包括:
- 没有消息的时候让线程休眠
- 有消息的时候唤醒线程
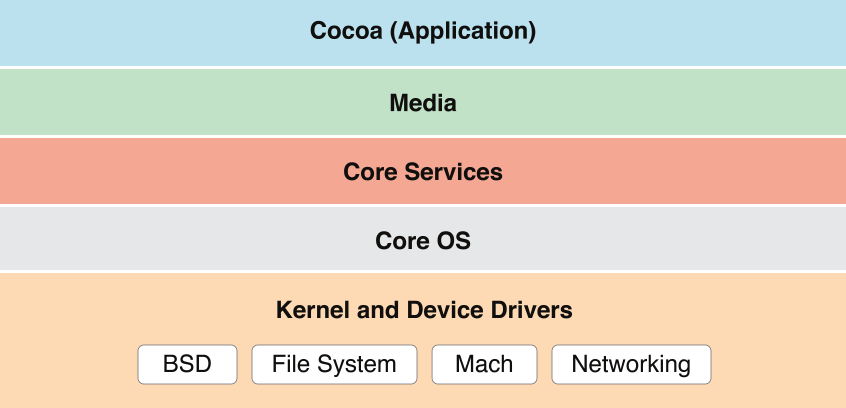
苹果官方将整个系统大致划分为上述4个层次:
- Cocoa 层:是直接向iOS应用程序提供各种基础功能的支持。其中的UIKit框架提供各种可视化控件供应用程序使用,如窗口、视图、视图控制器与各种用户控件等。另外UIKit也定义了应用程序的默认行为和事件处理结构。
- Media层:依赖于Core Services层提供的功能,主要负责图形与多媒体服务。它包含了CoreGraphics、Core Text、OpenGL ES、Core Animation、AVFoundation、Core Audio等与图形、视频和音频相关的功能模块。
- Core Services层:可称之为核心服务层,顾名思义,它提供诸如字符串管理、集合管理、网络操作、URL实用工具、联系人管理、偏好设置等服务。除此之外,它还提供很多基于硬件特性的服务,如GPS、加速仪、陀螺仪等。该层包含了Core Location、Core Motion、SystemConfiguration、Foundation与Core Foundation子模块。其中Foundation与Core Foundation子模块提供了对公共数据类型(字符串、集合等)的抽象,Core Foundation中的Core Data子模块可以实现对象图形管理与对象持久化。
- Core OS层:位于baiiOS框架的最底层,主要du包含内核、文件系统、网zhi络基础架构、安全管理、电源管理、设备驱动、线程管理、内存管理等。简而言之,该层提供了最低级的、系统级的服务。
- Darwin 即操作系统的核心,包括系统内核、驱动、Shell 等内容,这一层是开源的,其所有源码都可以在 opensource.apple.com 里找到。
OC 的 API 有很多个层级,开发者可以调用的属于用户层级的 API,向 _mach_msg() 这种属于内核层级的 API。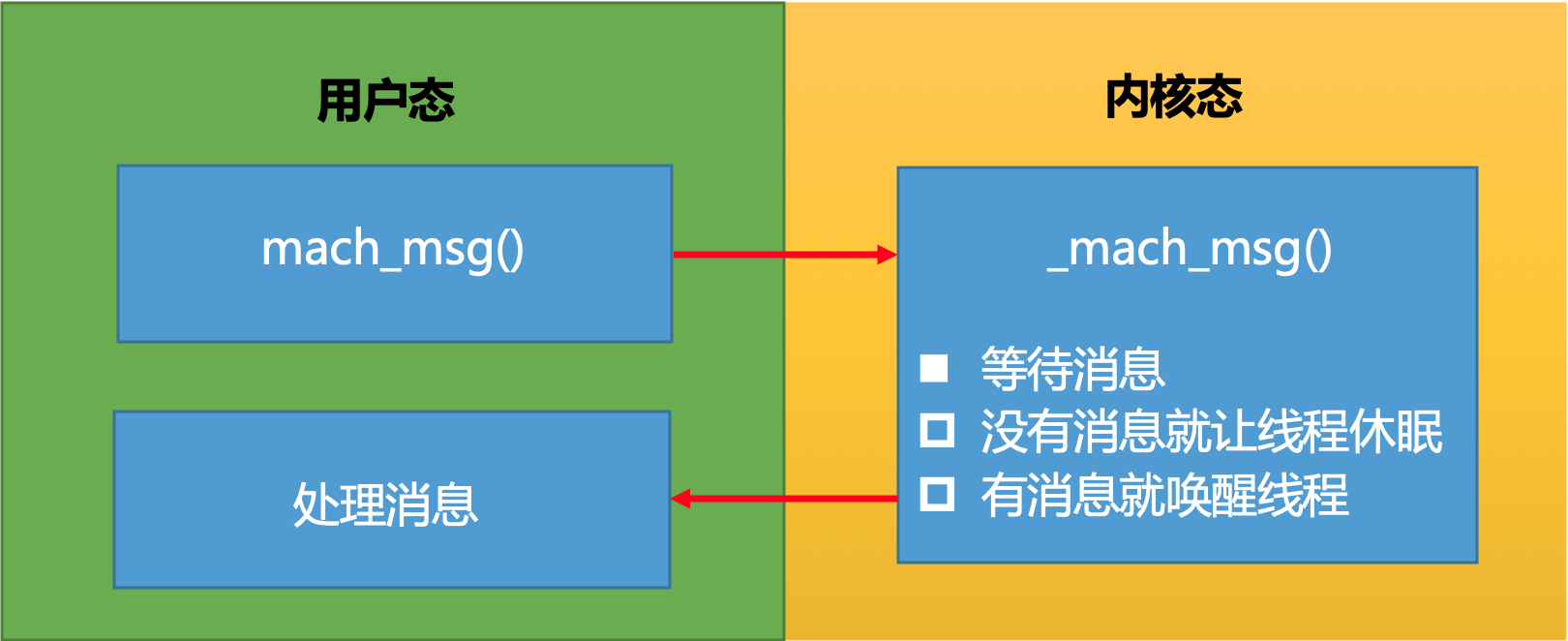
RunLoop 在实际开中的应用
NSTimer 失效
|
|
在控制器上加一个 UITextView 并上下拖拽,打印结果:
会发现定时器的打印在拖拽 TextView 时停止了,停止拖拽后,定时器的打印又继续进行了。这是因为 +scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:repeats:block: 方法会自动将创建的 timer 添加到 RunLoop 中,并将 RunLoop 的 mode 设置为 kCFRunLoopDefaultMode,而拖拽 TextView 使用的是 UITrackingRunLoopMode,但是 RunLoop 在同一时间只会执行一种 Mode,所以在拖拽 TextView 时 RunLoop 将 currentMode 切换成了 UITrackingRunLoopMode,NSTimer 自然就停止了。
解决方案:
通过 +timerWithTimeInterval:repeats:block: 方法创建 timer,然后手动添加到 RunLoop 中,并将 RunLoop 的 mode 设置为 NSRunLoopCommonModes。这个时候拖拽 TextView 就不会影响到 timer 了:
👉 思考:
为什么将 NSTimer 的 RunLoop 的 mode 设置为 NSRunLoopCommonModes 就可以正常执行了?NSRunLoopCommonModes 跟 UITrackingRunLoopMode 和 kCFRunLoopDefaultMode 有什么区别?
NSRunLoopCommonModes
|
|
NSRunLoopCommonModes 并不是一个真正的模式,只是一个标记。UITrackingRunLoopMode 和 kCFRunLoopDefaultMode 才是真正意义上的模式。
一般情况下添加 timer 到 RunLoop 时 mode 设置为 kCFRunLoopDefaultMode,timer 运行在 RunLoop 的 _modes 里的模式下,同时 timer 被保存到 mode 里的 _timers 中。当添加 timer 到 RunLoop 将 mode 设置为 NSRunLoopCommonModes 标记时,那么 timer 能在 _commonModes 里的模式下运行,同时 timer 被保存到了 RunLoop 的 _commonModeItems 中。
线程保活
|
|
点击屏幕,打印结果:
在线程中添加 RunLoop,可以保证线程不被释放,并在需要的时候工作,不需要的时候休眠。-(void)run 方法是线程调用的,所以在线程中添加 RunLoop 可以加在 -(void)run 方法中。RunLoop 不需要手动创建,在线程中第一次获取 RunLoop 的时候就会自动创建。
点击屏幕,打印结果:
可以看到线程还是被销毁了,这是因为 RunLoop 没有找到 Sources0/Sources1/Timer/Observer 就退出了,所以需要向 RunLoop 中添加任务:
打印结果:
从打印结果可以看到,线程停留在了 [[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] run]; 这一行,一直都没有打印 “—- end —-“。
因为 port 是 sources1 类型的事件,添加到 RunLoop 中却没有什么事情可做,RunLoop 就进入了休眠等待任务唤醒(没有退出),即 RunLoop 阻塞住了线程保证了线程不被释放,所以一直没有打印 “—- end —-“。
因为是在异步线程,所以不需要考虑 UITrackingRunLoopMode,直接设置为 NSDefaultRunLoopMode 就可以了。
为一直存活的线程添加任务:
点击屏幕,打印结果:
从打印结果可以看到,线程一直存在,并且可以重复执行任务。
上面👆的实现有以下几个问题:
NSThread 的初始化方法会对 self 进行强引用,导致 thread 和 self 循环引用问题。
1self.thread = [[YQThread alloc] initWithTarget:self selector:@selector(run)RunLoop 进入休眠并没有退出,所以一直不会打印 “—- end —-“,线程也就无法结束。
- NSRunLoop 的
-(void)run方法是无法停止的,它专门用于开启一个永不销毁的线程。-(void)run方法内部在重复创建 RunLoop。while 循环在第一次循环时会创建一个 RunLoop1 阻塞住 while 循环,RunLoop1 会在有任务时执行任务,没任务时休眠。当调用退出方法让 RunLoop1 退出后,while 循环会再次启动并创建一个新的 RunLoop2,逻辑同 RunLoop1。即退出了当前的 RunLoop 还会创建一个新的 RunLoop。伪代码实现:123while (1) {[[NSRunLoop currentRunLoop] runMode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode beforeDate:[NSDate distantFuture]];}
优化后的实现:
打印结果:
CFRunLoopStop(CFRunLoopGetCurrent()) 方法会退出当前的 RunLoop,此时 while 循环重新启动并在判断 isStop == YES 时停止循环,不会再创建新的 RunLoop。
打印结果中没有打印 “—- end —-“,线程也没有释放,是因为上面👆的实现还有以下几个问题:
performSelector:onThread:waitUntilDone方法的第三个参数 waitUntilDone 表示是否需要当前线程等待方法执行完成后再继续执行下一行。如果设置为 NO,则表示不需要等待,那么在控制器的-(void)dealloc方法里在 self 调用performSelector:onThread:waitUntilDone后,-(void)dealloc方法会继续往下执行,控制器被释放。那么在执行-(void)stopThread方法的时候再访问 self 就会出现坏内存访问的错误。while (!weakSelf.isStop)在控制器被销毁后也是成立的(while (!nil)==while (true)),所以 while 循环又会创建新的 RunLoop,线程还是无法释放。
最终实现:
打印结果:
线程的封装
为了方便使用,将线程封装成一个工具类,这样在使用的时候就不用管理线程的创建、保活和销毁了。
接口设计
方案一:创建一个 NSThread 的分类。这种方式需要用到关联对象创建 NSThread 对象,而且在外部使用时调用者可以调用 NSThread 提供的 API,封装性不够好。
方案二:创建一个 NSObject 管理类,里面管理一个 NSThread 对象。不直接继承 NSThread 的原因同上,为了控制调用者不能去访问 NSThread 提供的 API,保证 NSThread 相关的操作(创建、保活和销毁)全部且只能在管理类的内部操作,调用者只能调用由管理类提供的 API,这样就保证了封装性。
定义接口:
调用:
执行任务的方法也可以设计成 Block 的形式,代码会更精简:
内部实现
|
|
调用:
打印结果:
C语言方式实现
|
|
打印结果:
👉注意:
在创建上下文时,CFRunLoopSourceContext 是一个结构体,如果没有进行初始化,context 的内部的值可能会是一堆乱码。只有添加了初始化方法
{0},才能保证结构里内部的值是正常的数值:1CFRunLoopSourceContext context = {0};启动 RunLoop 时,第三个参数传 true 表示执行完 source 立即退出,传 false 表示执行完 source 不退出。在这里传 false 等同于 OC 实现中的 while 循环的作用。
1CFRunLoopRunInMode(kCFRunLoopDefaultMode, 1.0e10, false);
总结
讲讲 RunLoop,项目中有用到吗?
- RunLoop 保持程序的持续运行,没有 RunLoop 程序会马上退出,有了 RunLoop 程序并不会马上退出,而是保持运行状态;
- RunLoop 处理App中的各种事件(如:定时器(Timer)、PerformSelector、GCD、事件响应、手势识别、界面刷新、网络请求和 AutoreleasePool 等)。这些事件的代码最终都变成了 RunLoop 里的执行任务(sources0/sources1/timers),由 RunLoop 监控和执行;
- RunLoop 的休眠机制极大可能的节省了对CPU资源的占用,提高了程序性能;
- 每条线程都有唯一的一个与之对应的 RunLoop 对象。RunLoop 保存在一个全局的 Dictionary 里,线程作为 key,RunLoop 作为 value。线程刚创建时并没有 RunLoop 对象,RunLoop 会在第一次获取它时创建。RunLoop 会在线程结束时销毁。主线程的 RunLoop 已经自动获取(创建),子线程默认没有开启 RunLoop;
- RunLoop 启动时只能选择其中一个 Mode,作为 _currentMode。如果需要切换 Mode,只能退出当前 Loop,再重新选择一个 Mode 进入。一个 RunLoop 包含若干个 Mode,每个 Mode 又包含若干个 Sources0/Sources1/Timer/Observer。如果 Mode 里没有任何 Source0/Source1/Timer/Observer,RunLoop 会立马退出。
- RunLoop 有两种常见的 mode:
kCFRunLoopDefaultMode(NSDefaultRunLoopMode):App 的默认 Mode,通常主线程是在这个 Mode 下运行。
UITrackingRunLoopMode:界面跟踪 Mode,用于 ScrollView 追踪触摸滑动,保证界面滑动时不受其他 Mode 影响。(只有主线程需要考虑这种 mode)
NSRunLoopCommonModes:并不是一个真正的模式,只是一个标记。UITrackingRunLoopMode 和 kCFRunLoopDefaultMode 才是真正意义上的模式。一般情况下添加 timer 到 RunLoop 时 mode 设置为 kCFRunLoopDefaultMode,timer 运行在 RunLoop 的 _modes 里的模式下,同时 timer 被保存到 mode 里的 _timers 中。当添加 timer 到 RunLoop 将 mode 设置为 NSRunLoopCommonModes 标记时,那么 timer 能在 _commonModes 里的模式下运行,同时 timer 被保存到了 RunLoop 的 _commonModeItems 中。 RunLoop 的休眠唤醒逻辑是通过调用一个内核方法
mach_msg()实现的。项目中使用 RunLoop 的地方比较少,主要有解决 NSTimer 失效问题,自定义线程保活。
RunLoop 内部实现逻辑?
RunLoop 启动时只能选择其中一个 Mode,作为 _currentMode。如果需要切换 Mode,只能退出当前 Loop,再重新选择一个 Mode 进入。一个 RunLoop 包含若干个 Mode,每个 Mode 又包含若干个 Sources0/Sources1/Timer/Observer。如果 Mode 里没有任何 Source0/Source1/Timer/Observer,RunLoop 会立马退出。
RunLoop 的休眠唤醒逻辑是通过调用一个内核方法
mach_msg()实现的。
RunLoop 和线程的关系?
每条线程都有唯一的一个与之对应的 RunLoop 对象。RunLoop 保存在一个全局的 Dictionary 里,线程作为 key,RunLoop 作为 value。线程刚创建时并没有 RunLoop 对象,RunLoop 会在第一次获取它时创建。RunLoop 会在线程结束时销毁。主线程的 RunLoop 已经自动获取(创建),子线程默认没有开启 RunLoop;timer 与 RunLoop 的关系?
一般情况下添加 timer 到 RunLoop 时 mode 设置为 kCFRunLoopDefaultMode,timer 运行在 RunLoop 的 _modes 里的模式下,同时 timer 被保存到 mode 里的 _timers 中。当添加 timer 到 RunLoop 将 mode 设置为 NSRunLoopCommonModes 标记时,那么 timer 能在 _commonModes 里的模式下运行,同时 timer 被保存到了 RunLoop 的 _commonModeItems 中。程序中添加每3秒响应一次的 NSTimer,当拖动 tableview 时 timer 可能无法响应要怎么解决?
通过 +timerWithTimeInterval:repeats:block: 方法创建 timer,然后手动添加到 RunLoop 中,并将 RunLoop 的 mode 设置为 NSRunLoopCommonModes。这个时候拖拽 TextView 就不会影响到 timer 了。原因在上面“timer 与 RunLoop 的关系”。RunLoop 是怎么响应用户操作的, 具体流程是什么样的?

说说 RunLoop 的几种状态
123456789typedef CF_OPTIONS(CFOptionFlags, CFRunLoopActivity) {kCFRunLoopEntry = (1UL << 0), //即将进入LoopkCFRunLoopBeforeTimers = (1UL << 1), //即将处理TimerkCFRunLoopBeforeSources = (1UL << 2), //即将处理SourcekCFRunLoopBeforeWaiting = (1UL << 5), //即将进入休眠kCFRunLoopAfterWaiting = (1UL << 6), //刚从休眠中唤醒kCFRunLoopExit = (1UL << 7), //即将推出LoopkCFRunLoopAllActivities = 0x0FFFFFFFU};RunLoop 的 mode 作用是什么?
mode 是 RunLoop 的运行模式。RunLoop 启动时只能选择其中一个 Mode,作为 _currentMode。如果需要切换 Mode,只能退出当前 Loop,再重新选择一个 Mode 进入。一个 RunLoop 包含若干个 Mode,每个 Mode 又包含若干个 Sources0/Sources1/Timer/Observer。不同组(不同mode)的 Sources0/Sources1/Timer/Observer 能分隔开来,互不影响。如果 Mode 里没有任何 Sources0/Sources1/Timer/Observer,RunLoop 会立马退出。RunLoop 将 OC 代码转换成了 Sources0/Sources1/Timer/Observer 保存到不同的 mode 里,并且循环监测并执行它们。比如:定时器(Timer)、PerformSelector、GCD、事件响应、手势识别、界面刷新、网络请求和 AutoreleasePool 等都是在进入休眠前完成的。