队列是一种特殊的线性表,特殊之处在于它只允许在表的前端(front)进行删除操作,而在表的后端(rear)进行插入操作,和栈一样,队列是一种操作受限制的线性表。进行插入操作的端称为队尾,进行删除操作的端称为队头。
队列
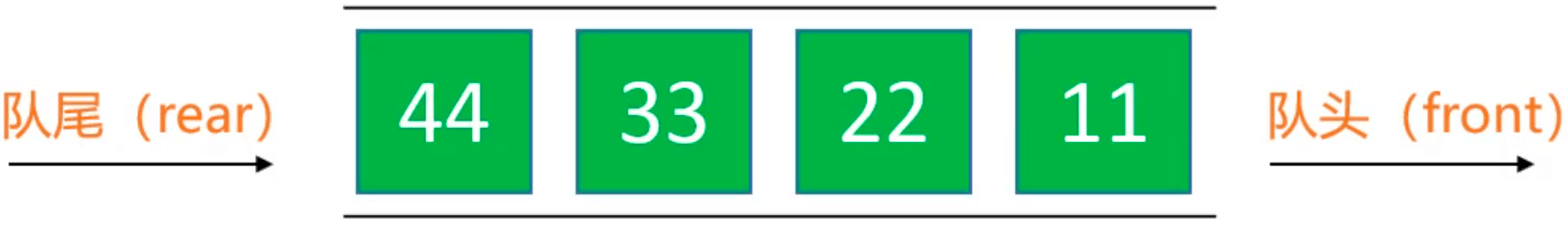
队列是一种特殊的线性表,只能在头尾两端进行操作:
队尾(rear):只能从队尾添加元素,一般叫做 enQueue,入队;
队头(front):只能从队头移除元素,一般叫做 deQueue,出队;
先进先出的原则,First In First Out,FIFO
入队: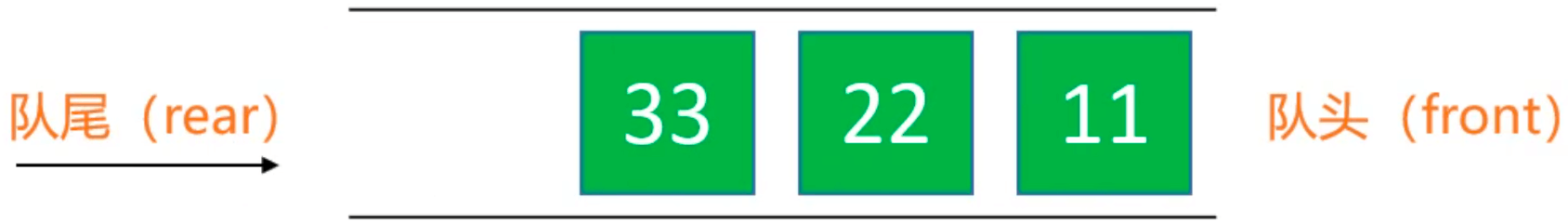
出队:
通过双向链表实现
动态数组和链表都可以用来实现队列。因为队列主要是在头尾操作元素,所以优先使用双向链表实现队列。
测试:
打印结果:
通过栈实现
232. 用栈实现队列
入队: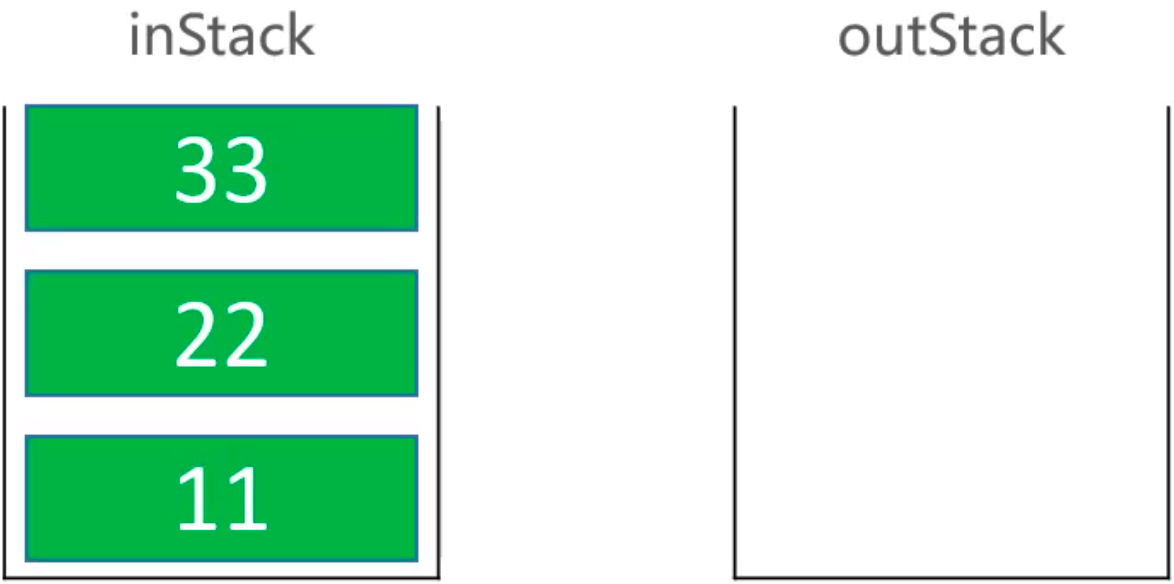
出队: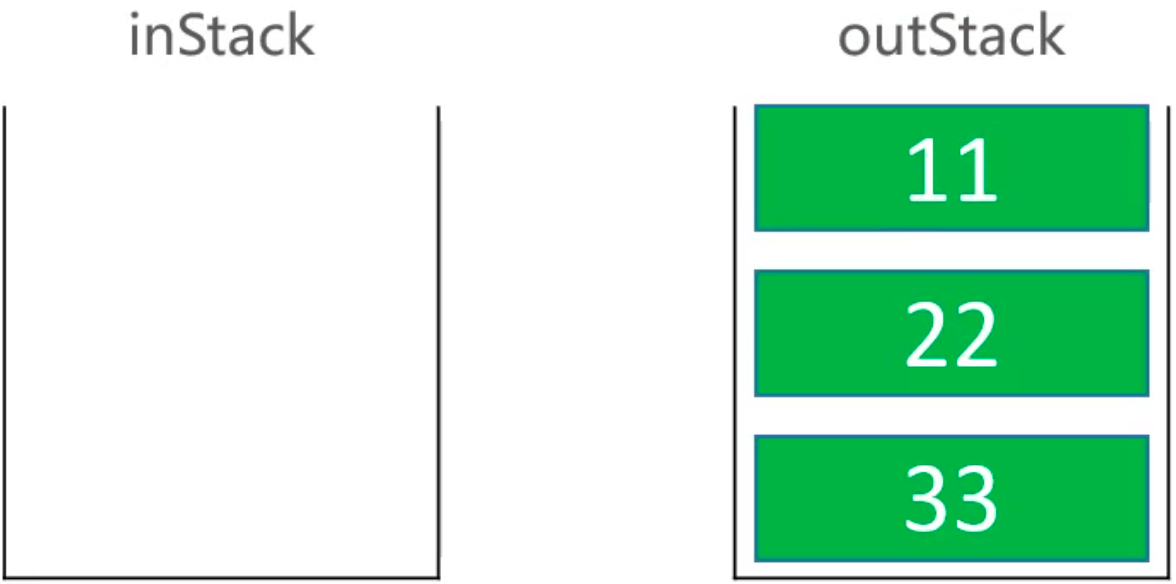
源码分析
Queue.class 文件里只有定义没有实现:
在 Queue.class 文件里的注释可以看到,Queue 是在 LinkedList.class 里实现的:
双端队列
双端队列是能在头尾两端进行添加、删除操作的队列。
测试:
打印结果:
源码分析
同 Queue 的源码分析👆。
循环队列
循环队列底层使用数组实现的,实现思路可以参考链表中的动态数组优化。
对于一个队列: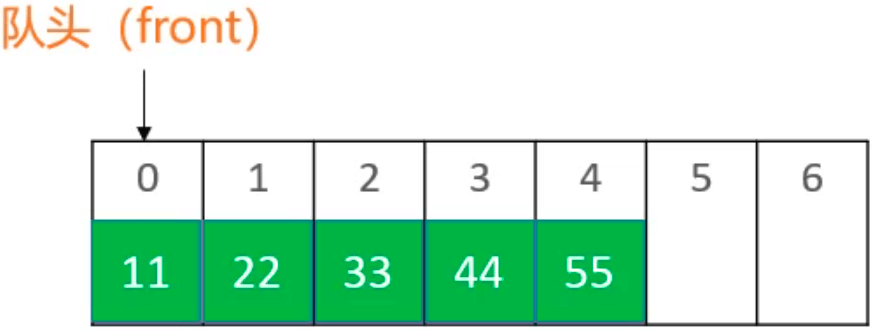
队头的两个元素依次出栈,front 指向 2: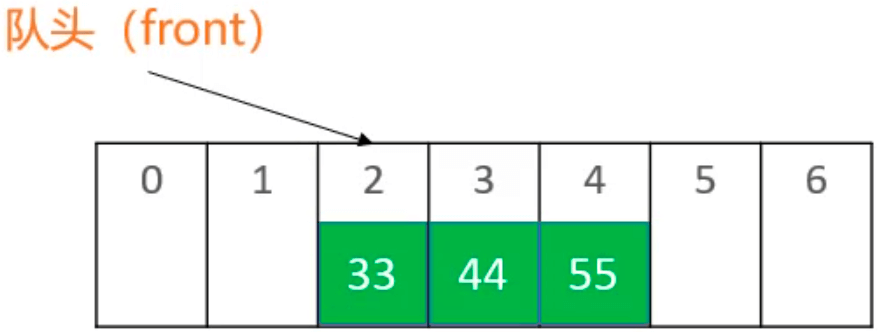
队尾依次入栈66、77、88、99,其中88、99超出数组大小,放到数组的 0 和 1 处((front + index) % elements.length):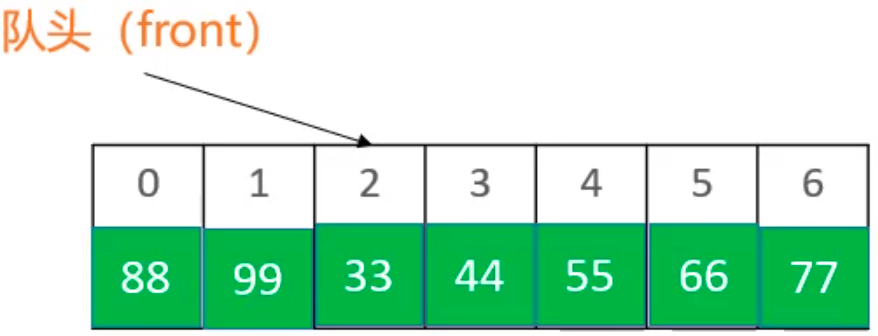
ps:% 运算符的优化 - 已知 n>=0,m>=0,n < 2m,则 n%m 等价于 n - (m > n ? 0 : m)。
代码实现:
测试:
循环双端队列
循环双端队列可以进行两端添加、删除操作的循环队列,实现思路可以循环队列和链表中的动态数组优化。
对于一个队列:
队头入栈22,因为 front 指向的位置是队列 0 的位置,在 front 的左边入栈,也就相当于在队列 -1 的位置入栈((front - 1) % elements.length):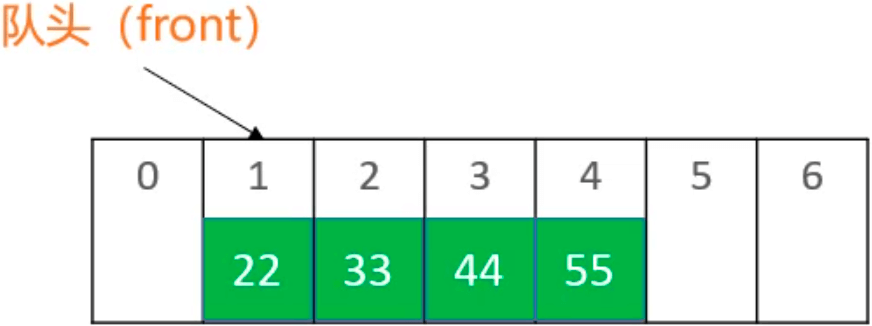
代码实现:
测试:
练习
|
|
.