AVL树是最先发明的自平衡二叉查找树。在AVL树中任何节点的两个子树的高度最大差别为1,所以它也被称为高度平衡树。增加和删除可能需要通过一次或多次树旋转来重新平衡这个树。AVL树得名于它的发明者G. M. Adelson-Velsky和E. M. Landis,他们在1962年的论文《An algorithm for the organization of information》中发表了它。
平衡二叉搜索树(Balanced Binary Search Tree)
二叉搜索树的复杂度分析
依次添加节点 7、4、9、2、5、8、11 得到的二叉搜索树,添加、删除和搜索操作的复杂度跟二叉搜索树的高度有关,O(h) == O(logn)。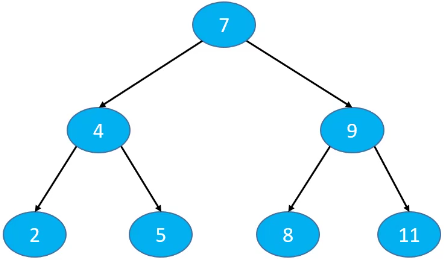
依次添加节点 2、4、5、7、8、9、11 得到的二叉搜索树,添加、删除和搜索操作的复杂度跟节点个数有关,O(h) == O(n)。二叉搜索树退化成了链表。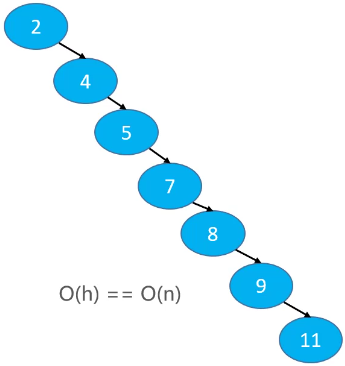
当 n 比较大时,两者的性能差异比较大。如 n == 1000000 时,二叉搜索树的最低高度是 20。
平衡(Balance)
平衡:当节点数固定时,左右子树的高度越接近,这课二叉树就越平衡(高度越低)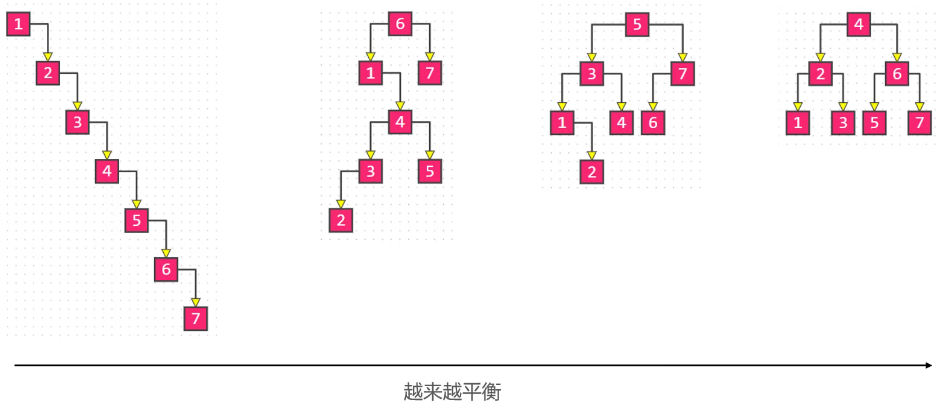
理想平衡
最理想的平衡,就是像完全二叉树、满二叉树那样,高度是最小的。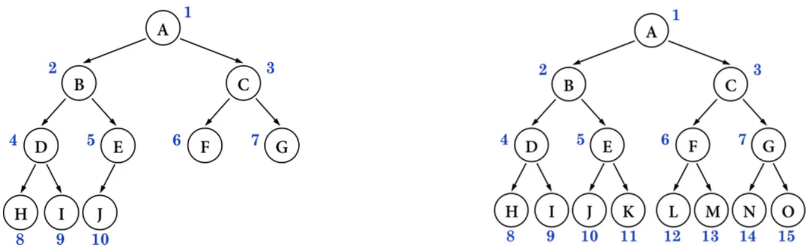
如何改进二叉搜索树?
因为节点的添加、删除顺序是无法限制的,可以认为是随机的,所以改进方案是:在节点的添加、删除操作之后,想办法让二叉搜索树恢复平衡(减小树的高度)。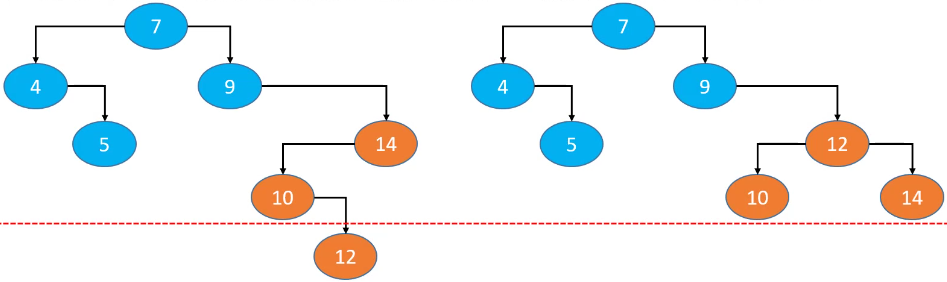
如果按照图中的调整方式再继续调整其它节点的位置,就可以达到理想平衡。但是调整的次数太多,反而增加了时间复杂度。所以,比较合理的改进方案是:用尽量少的调整次数达到适合平衡即可,即平衡二叉搜索树。
经典的平衡二叉搜索树
平衡二叉搜索树简称:BBST。
AVL 树
Windows NT 内核中广泛使用
红黑树
- C++ STL(比如:map、set);
- Java 的 TreeMap、TreeSet、HashMap、HashSet;
- Linux 的进度调整;
- Ngix 的 timer 管理;
AVL 树、红黑树一般也称为自平衡的二叉搜索树。
AVL 树
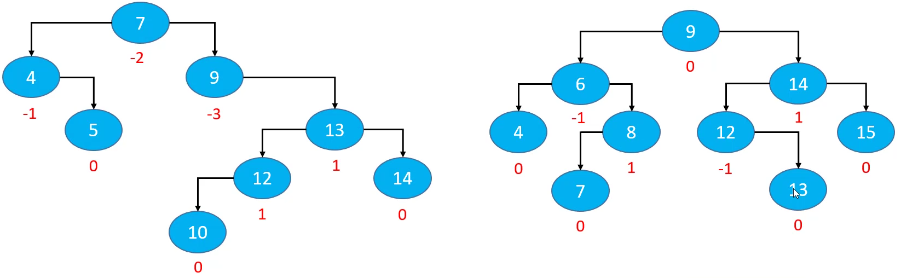
平衡因子
平衡因子(Balance Factor):某节点的左右子树的高度差。
AVL树的特点:
- 每个节点的平衡因子只可能是 1、0、-1(绝对值 <= 1,如果超过 1,称之为“失衡”);
- 每个节点的左右子树高度差不超过 1;
- 搜索、添加和删除的时间复杂度是 O(logn);
继承结构
创建 AVLTree 继承自 BST。红黑树同理,创建 RBTree 继承自 BST。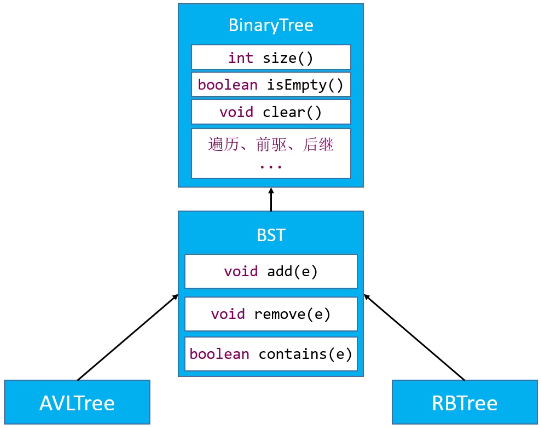
添加导致的失衡
下面这个子树原本是平衡的,添加节点13后出现失衡。最坏情况是导致节点13的所有祖先节点都失衡(14、15、9及其父节点)。节点13的父节点、非祖先节点都不可能失衡。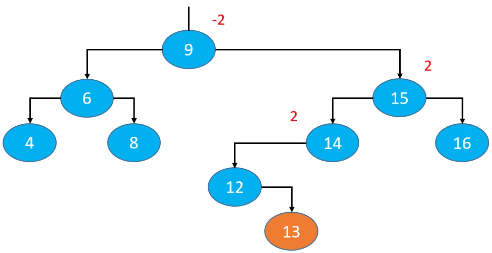
LL-右旋转(单旋)
n(node)、p(paren)和g(grandparent),T0(n的左子树)、T1(n的右子树)、T2(p的右子树)、T3(g的右子树)。
g.left = p.rightp.right = g- 让
p成为这棵子树的根节点 - 更新
T2、p、g的 parent 属性 - 先后更新
g、p的高度
旋转后的子树又恢复了平衡,仍然是一棵二叉搜索树:T0 < g < T1 < p < T2 < n < T3。
注意:一定要修改 T2、p、g 的 parent 属性;依次更新 g、p 的高度(因为旋转后,g 是 p 的右子树,所以先计算子树的高度,然后 +1 就是 p 的高度)。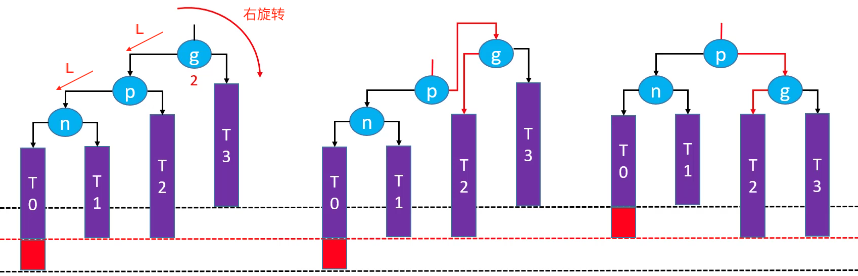
RR-左旋转(单旋)
g.right = p.leftp.left = g- 让
p成为这个子树的根节点 - 更新
T1、p、g的 parent 属性 - 先后更新
g、p的高度
旋转后的子树又恢复了平衡,仍然是一棵二叉搜索树:T0 < g < T1 < p < T2 < n < T3。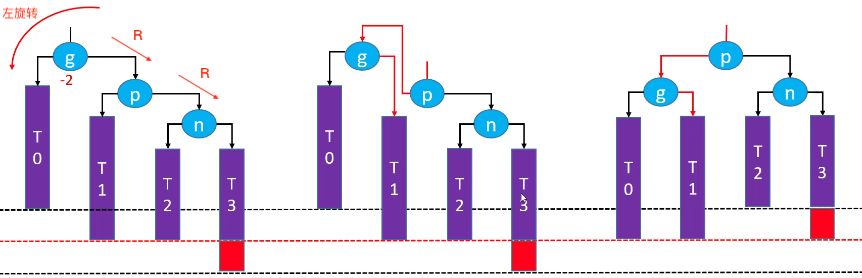
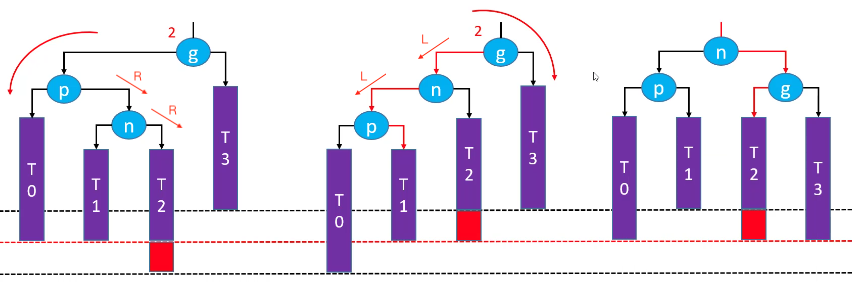
LR-RR左旋转,LL右旋转(双旋)
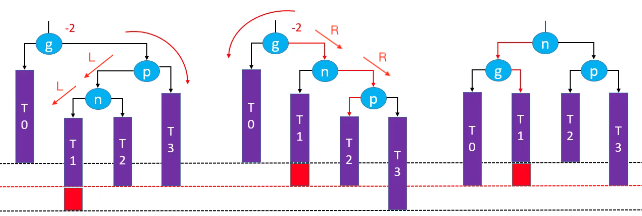
RL-LL右旋转,RR左旋转(双旋)
CODE
|
|
添加处理(affterAdd)
在节点的添加、删除操作之后,先办法让二叉搜索树恢复平衡(减小树的高度)。
在 BST 定义:
在 AVLTree 实现:
AVLNode
- 因为 Node 里用不到 height 属性,所以定义 AVLNode 继承自 Node,添加 height 属性;
isBalanced()是否平衡;updateHeight()更新高度;tallerChild()高度较高的子树,用于恢复平衡;12345678910111213141516171819202122232425262728private static class AVLNode<E> extends Node<E> {//叶子节点高度默认1int height = 1;public AVLNode(E element, Node<E> parent) {super(element, parent);}public int balanceFactor() {int leftHeight = left == null ? 0 : ((AVLNode<E>)left).height;int rightHeight = right == null ? 0 : ((AVLNode<E>)right).height;return leftHeight - rightHeight;}public void updateHeight() {int leftHeight = left == null ? 0 : ((AVLNode<E>)left).height;int rightHeight = right == null ? 0 : ((AVLNode<E>)right).height;height= 1 + Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight);}public Node<E> tallerChild() {int leftHeight = left == null ? 0 : ((AVLNode<E>)left).height;int rightHeight = right == null ? 0 : ((AVLNode<E>)right).height;if (leftHeight > rightHeight) return left;if (leftHeight < rightHeight) return right;return isLeftChild() ? left : right;}}
恢复平衡
|
|
统一所有旋转操作
综上所述,失去平衡的情况有四种:LL、RR、LR 和 RL。这四种情况再恢复平衡后是一样的结构:
d是根节点;b和f分别是d的左子树和右子树;a和c分别是b的左子树和右子树,e和g分别是f的左子树和右子树;
(a 和 g 在操作前后是没有变化的,所以这里的 a 和 g 可以不做处理)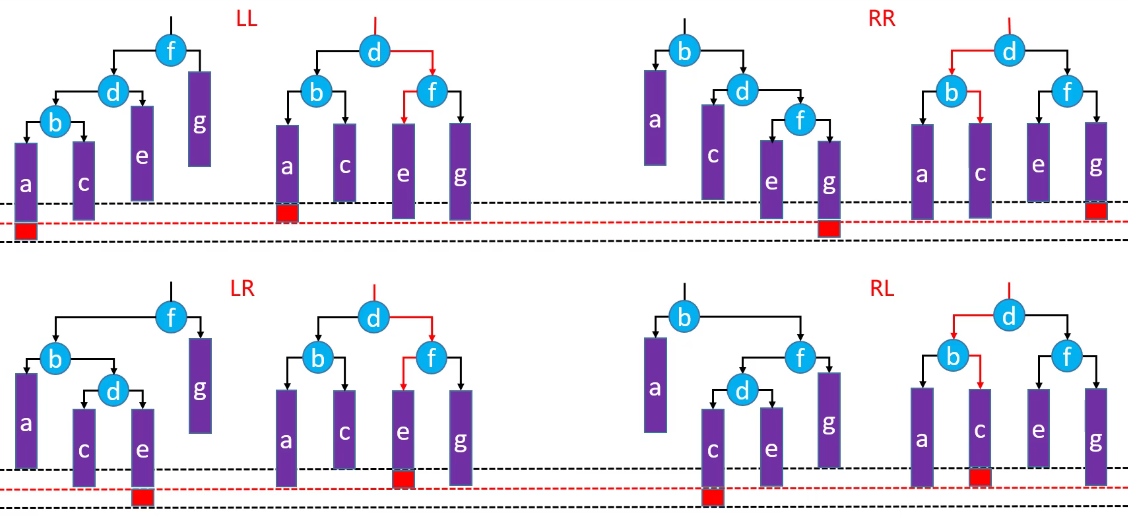
删除导致的失衡
删除操作可能会导致父节点或祖先节点失衡(只有一个节点会失衡),其他节点都不可能失衡。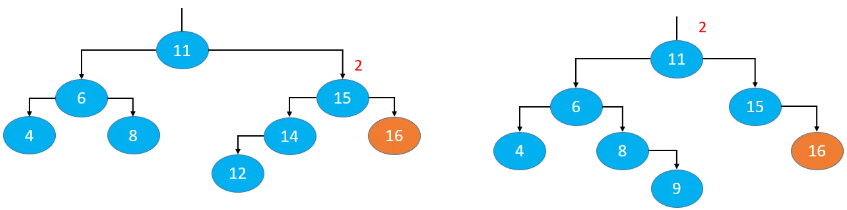
LL-右旋转(单旋)
删除红色节点: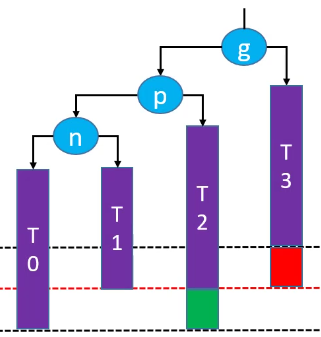
右旋转后恢复平衡(绿色节点存在的情况下):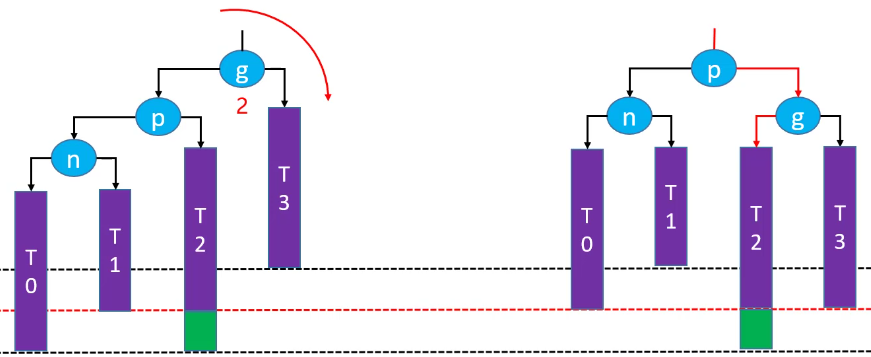
右旋转后,祖先节点失去平衡(绿色节点不存在的情况下):
如果绿色节点不存在,更高层的祖先节点可能也会失衡,需要再次恢复平衡,然后又可能导致更高层次的祖先节点失衡。极端情况下,所有祖先节点都需要进行恢复平衡的操作,共 O(logn) 次调整。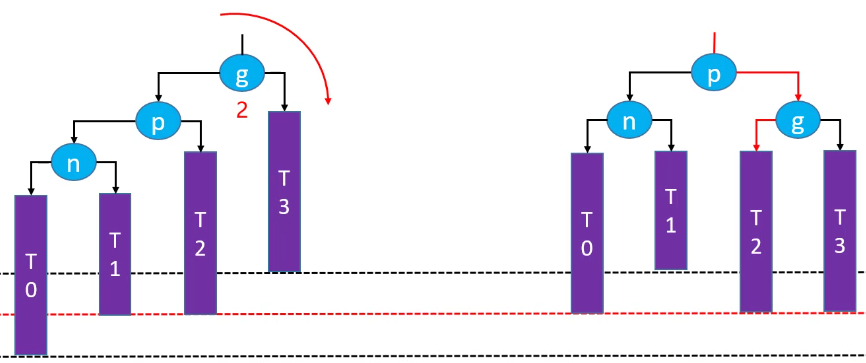
RR-左旋转(单旋)
删除红色节点: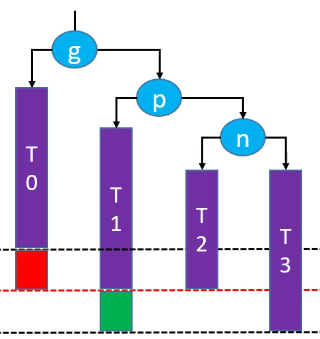
左旋转后恢复平衡(绿色节点存在的情况下):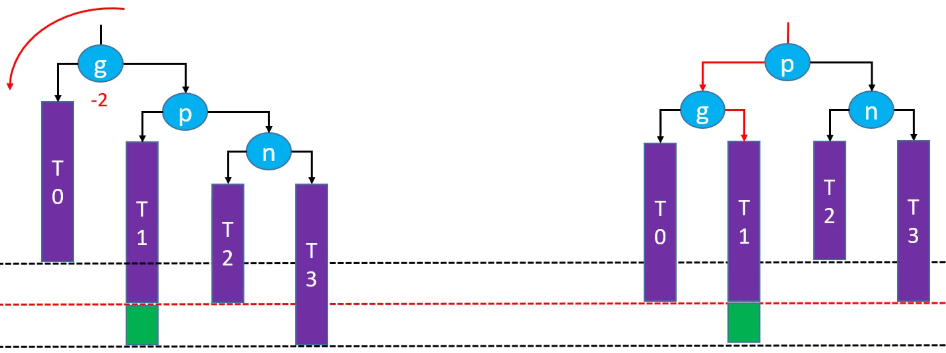
左旋转后,祖先节点失去平衡(绿色节点不存在的情况下):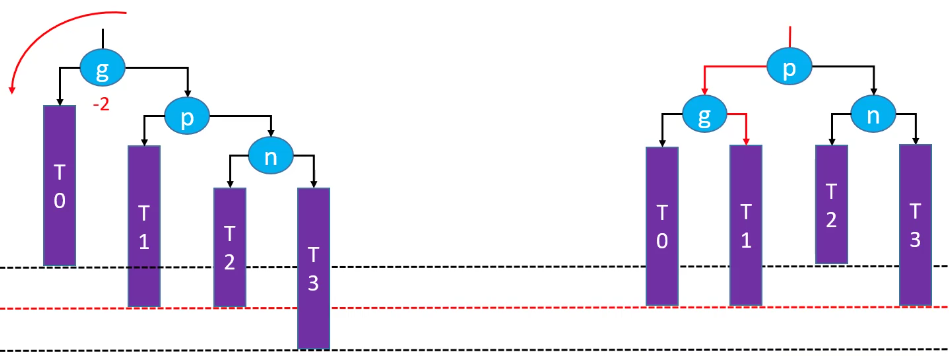
LR-RR左旋转,LL右旋转(双旋)
删除红色节点: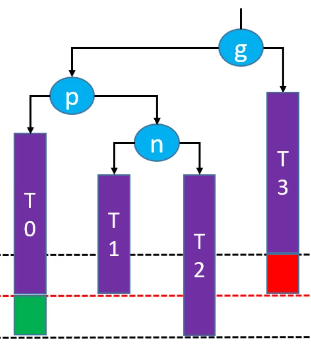
先左旋再右旋恢复平衡(绿色节点存在的情况下):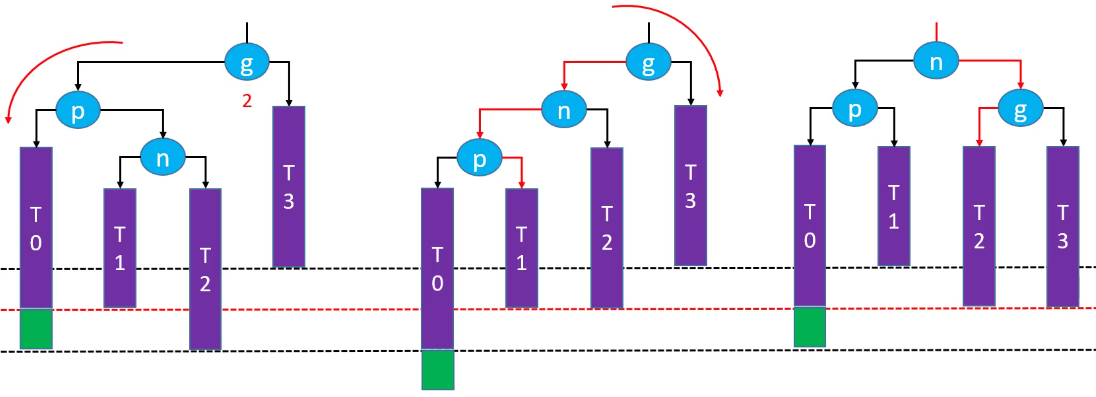
先左旋再右旋后,祖先节点失去平衡(绿色节点不存在的情况下):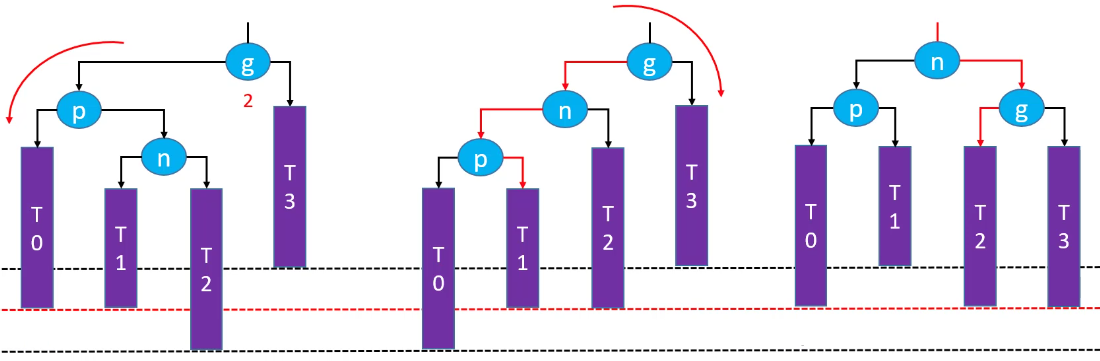
RL-LL右旋转,RR左旋转(双旋)
删除红色节点: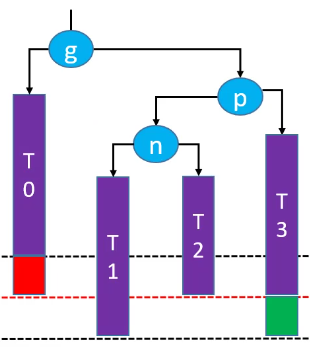
先右旋在左旋恢复平衡(绿色节点存在的情况下):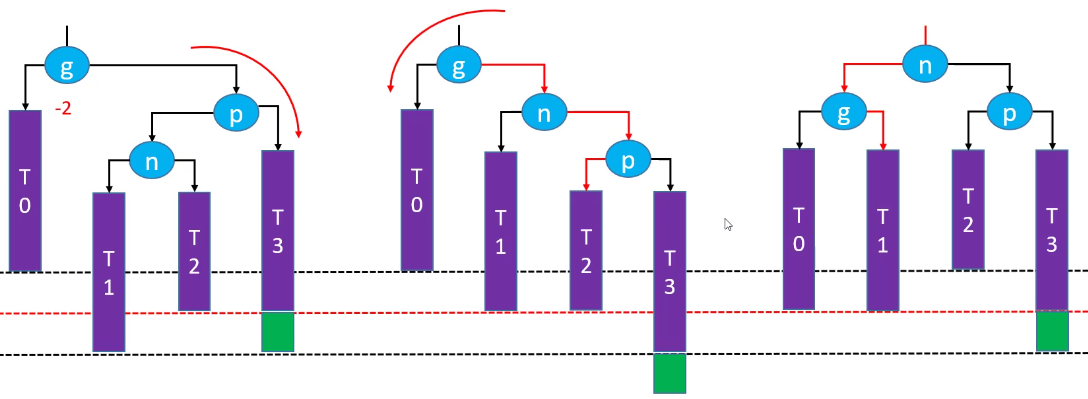
先右旋再左旋,祖先节点失去平衡(绿色节点不存在的情况下):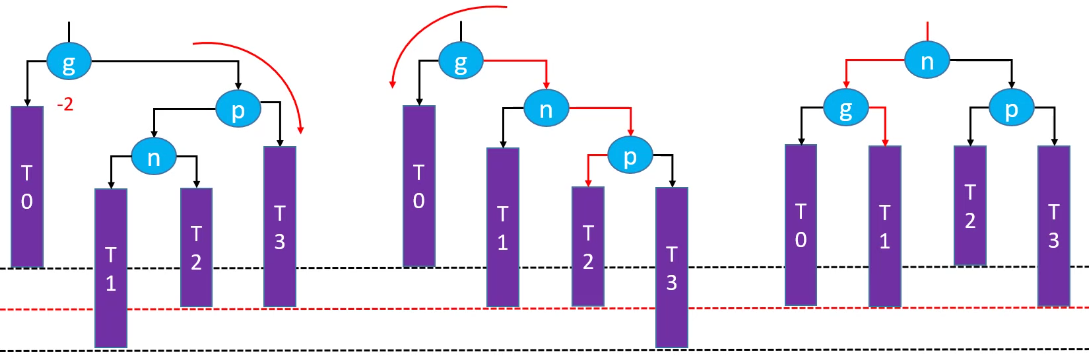
CODE
|
|
删除后处理(afterRemove)
在 BST 定义:
在 AVLTree 实现:
总结
添加
可能会导致所有祖先节点都失衡;
只要让高度最低的失衡节点恢复平衡,整棵树就恢复平衡【仅需O(1)次调整】。删除
可能会导致父节点或祖先节点失衡(只有1个节点会失衡);
恢复平衡后,可能会导致更高层的祖先节点失衡【最多需要O(logn)次调整】。平均时间复杂度
搜索:O(logn);
添加:O(logn),仅需O(1)次的旋转操作;
删除:O(logn),最多需要O(logn)次的旋转操作。
练习
110. 平衡二叉树